Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
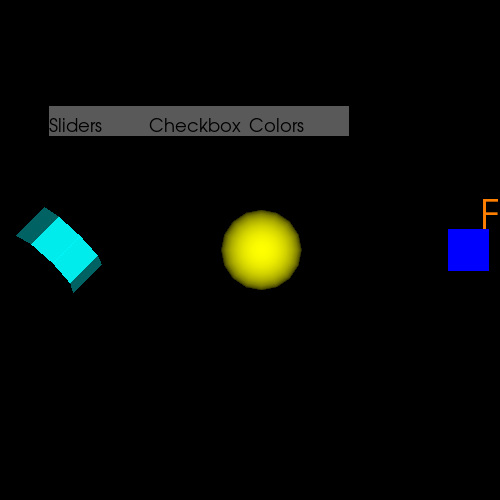
Tab UI#
This example shows how to use the Tab UI. We will demonstrate how to create Tabs for:
Slider controls for a Cube
Checkboxes for Cylinder and Sphere
Color combobox for Fury.
First, some imports.
import numpy as np
import fury
First we need to fetch some icons that are included in FURY.
fury.data.fetch_viz_icons()
Data size is approximately 12KB
Dataset is already in place. If you want to fetch it again please first remove the folder /Users/skoudoro/.fury/icons
({'icomoon.tar.gz': ('https://digital.lib.washington.edu/researchworks/bitstream/handle/1773/38478/icomoon.tar.gz', 'BC1FEEA6F58BA3601D6A0B029EB8DFC5F352E21F2A16BA41099A96AA3F5A4735')}, '/Users/skoudoro/.fury/icons')
First, we create the Tab UI.
tab_ui = fury.ui.TabUI(position=(49, 94), size=(300, 300), nb_tabs=3, draggable=True)
We can also define the position of the Tab Bar. By default the Tab Bar is positioned at top
tab_ui.tab_bar_pos = "bottom"
Slider Controls for a Cube for Tab Index 0#
Now we prepare content for the first tab.
ring_slider = fury.ui.RingSlider2D(initial_value=0, text_template="{angle:5.1f}°")
line_slider_x = fury.ui.LineSlider2D(
initial_value=0,
min_value=-10,
max_value=10,
orientation="horizontal",
text_alignment="Top",
)
line_slider_y = fury.ui.LineSlider2D(
initial_value=0,
min_value=-10,
max_value=10,
orientation="vertical",
text_alignment="Right",
)
cube = fury.actor.box(
centers=np.array([[10, 0, 0]]),
directions=np.array([[0, 1, 0]]),
colors=np.array([[0, 0, 1]]),
scales=np.array([[1, 1, 1]]),
)
cube_x = 0
cube_y = 0
def rotate_cube(slider):
angle = slider.value
previous_angle = slider.previous_value
rotation_angle = angle - previous_angle
cube.RotateX(rotation_angle)
def translate_cube_x(slider):
global cube_x, cube_y
cube_x = slider.value
cube.SetPosition(cube_x, cube_y, 0)
def translate_cube_y(slider):
global cube_x, cube_y
cube_y = slider.value
cube.SetPosition(cube_x, cube_y, 0)
ring_slider.on_change = rotate_cube
line_slider_x.on_change = translate_cube_x
line_slider_y.on_change = translate_cube_y
After defining content, we define properties for the tab.
tab_ui.tabs[0].title = "Sliders"
tab_ui.add_element(0, ring_slider, (0.3, 0.3))
tab_ui.add_element(0, line_slider_x, (0.0, 0.0))
tab_ui.add_element(0, line_slider_y, (0.0, 0.1))
CheckBoxes For Cylinder and Sphere for Tab Index 1#
Now we prepare content for second tab.
cylinder = fury.actor.cylinder(
centers=np.array([[0, 0, 0]]),
directions=np.array([[1, 1, 0]]),
colors=np.array([[0, 1, 1]]),
radius=1.0,
)
sphere = fury.actor.sphere(centers=np.array([[5, 0, 0]]), colors=(1, 1, 0))
figure_dict = {"cylinder": cylinder, "sphere": sphere}
checkbox = fury.ui.Checkbox(labels=["cylinder", "sphere"])
# Get difference between two lists.
def sym_diff(l1, l2):
return list(set(l1).symmetric_difference(set(l2)))
# Set Visibility of the figures
def set_figure_visiblity(checkboxes):
checked = checkboxes.checked_labels
unchecked = sym_diff(list(figure_dict), checked)
for visible in checked:
figure_dict[visible].SetVisibility(True)
for invisible in unchecked:
figure_dict[invisible].SetVisibility(False)
checkbox.on_change = set_figure_visiblity
After defining content, we define properties for the tab.
tab_ui.tabs[1].title = "Checkbox"
tab_ui.add_element(1, checkbox, (0.2, 0.2))
Color Combobox for Fury for Tab Index 2#
Now we prepare content for third tab.
label = fury.ui.TextBlock2D(
position=(600, 300),
font_size=40,
color=(1, 0.5, 0),
justification="center",
vertical_justification="top",
text="FURY rocks!!!",
)
colors = {
"Violet": (0.6, 0, 0.8),
"Indigo": (0.3, 0, 0.5),
"Blue": (0, 0, 1),
"Green": (0, 1, 0),
"Yellow": (1, 1, 0),
"Orange": (1, 0.5, 0),
"Red": (1, 0, 0),
}
color_combobox = fury.ui.ComboBox2D(
items=list(colors.keys()),
placeholder="Choose Text Color",
size=(250, 150),
draggable=True,
)
def change_color(combobox):
label.color = colors[combobox.selected_text]
color_combobox.on_change = change_color
After defining content, we define properties for the tab.
tab_ui.tabs[2].title = "Colors"
tab_ui.add_element(2, color_combobox, (0.1, 0.3))
Define on_change & on_collapsed methods for tab ui to perform certain tasks while active tab is changed or when the tab is collapsed. Note: Tab UI can be collapsed by right clicking on it.
def hide_actors(tab_ui):
if tab_ui.tabs[tab_ui.active_tab_idx].title == "Sliders":
cube.SetVisibility(True)
cylinder.SetVisibility(False)
sphere.SetVisibility(False)
label.set_visibility(False)
elif tab_ui.tabs[tab_ui.active_tab_idx].title == "Checkbox":
cube.SetVisibility(False)
set_figure_visiblity(checkbox)
label.set_visibility(False)
else:
cube.SetVisibility(False)
cylinder.SetVisibility(False)
sphere.SetVisibility(False)
label.set_visibility(True)
def collapse(tab_ui):
if tab_ui.collapsed:
cube.SetVisibility(False)
cylinder.SetVisibility(False)
sphere.SetVisibility(False)
label.set_visibility(False)
tab_ui.on_change = hide_actors
tab_ui.on_collapse = collapse
Next we prepare the scene and render it with the help of show manager.
sm = fury.window.ShowManager(size=(800, 500), title="Viz Tab")
sm.scene.add(tab_ui, cube, cylinder, sphere, label)
# To interact with the ui set interactive = True
interactive = False
if interactive:
sm.start()
fury.window.record(scene=sm.scene, size=(500, 500), out_path="viz_tab.png")
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.096 seconds)
