Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Bezier Interpolator#
Keyframe animation using cubic Bezier interpolator.
import numpy as np
import fury
Position interpolation using cubic Bezier curve#
Cubic bezier curve is a widely used method for interpolating motion paths. This can be achieved using positions and control points between those positions.
scene = fury.window.Scene()
showm = fury.window.ShowManager(
scene=scene, size=(900, 768), reset_camera=False, order_transparent=True
)
Cubic Bezier curve parameters#
In order to make a cubic bezier curve based animation, you need four values for every keyframe:
1- Timestamp: The time that the keyframe is assigned to.
2- Value: The value of the keyframe. This might be position, quaternion, or scale value.
3- In control point: The control point used when the value is the destination value.
4- Out control point: The control point used when the value is the departure value:
keyframe_1 = {"value": [-2, 0, 0], "out_cp": [-15, 6, 0]}
keyframe_2 = {"value": [18, 0, 0], "in_cp": [27, 18, 0]}
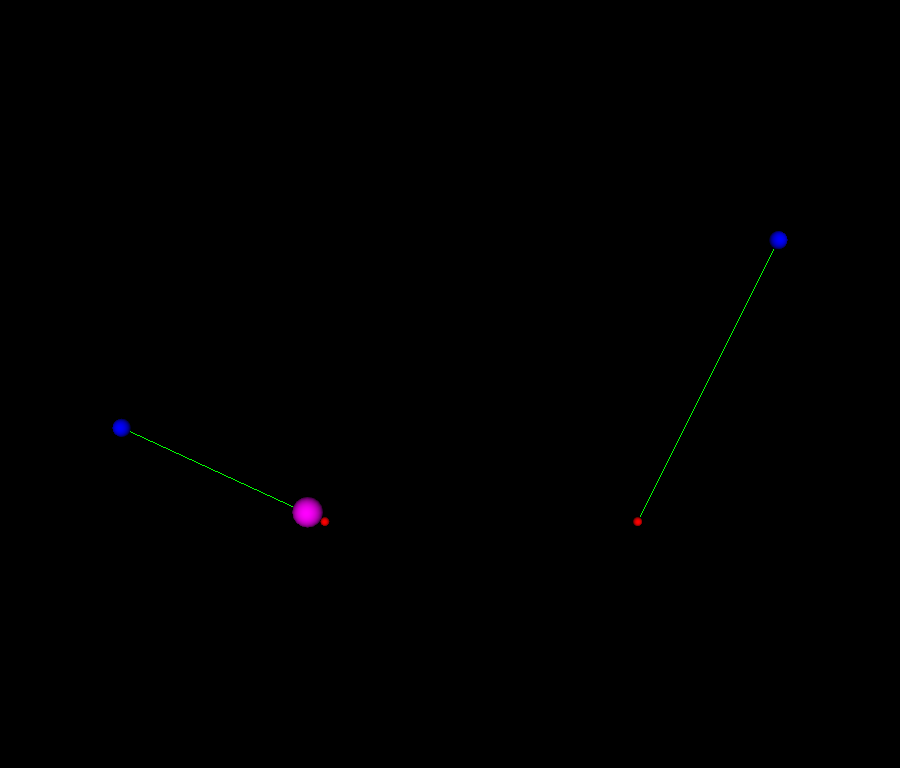
Visualizing points
pts_actor = fury.actor.sphere(
np.array([keyframe_1.get("value"), keyframe_2.get("value")]), (1, 0, 0), radii=0.3
)
Visualizing the control points
cps_actor = fury.actor.sphere(
np.array([keyframe_2.get("in_cp"), keyframe_1.get("out_cp")]), (0, 0, 1), radii=0.6
)
Visualizing the connection between the control points and the points
cline_actor = fury.actor.line(
np.array([list(keyframe_1.values()), list(keyframe_2.values())]),
colors=np.array([0, 1, 0]),
)
Initializing an Animation and adding sphere actor to it.
animation = fury.animation.Animation()
sphere = fury.actor.sphere(np.array([[0, 0, 0]]), (1, 0, 1))
animation.add_actor(sphere)
Setting Cubic Bezier keyframes#
Cubic Bezier keyframes consists of 4 data per keyframe Timestamp, position, in control point, and out control point.
In control point is the cubic bezier control point for the associated position when this position is the destination position.
Out control point is the cubic bezier control point for the associated position when this position is the origin position or departing position.
Note: If a control point is not provided or set None, this control point will be the same as the position itself.
animation.set_position(
0.0, np.array(keyframe_1.get("value")), out_cp=np.array(keyframe_1.get("out_cp"))
)
animation.set_position(
5.0, np.array(keyframe_2.get("value")), in_cp=np.array(keyframe_2.get("in_cp"))
)
Changing position interpolation into cubic bezier interpolation
animation.set_position_interpolator(fury.animation.cubic_bezier_interpolator)
Adding the visualization actors to the scene.
scene.add(pts_actor, cps_actor, cline_actor)
Adding the animation to the ShowManager
showm.add_animation(animation)
interactive = False
if interactive:
showm.start()
fury.window.record(
scene=scene,
out_path="viz_keyframe_animation_bezier_1.png",
size=(900, 768),
)
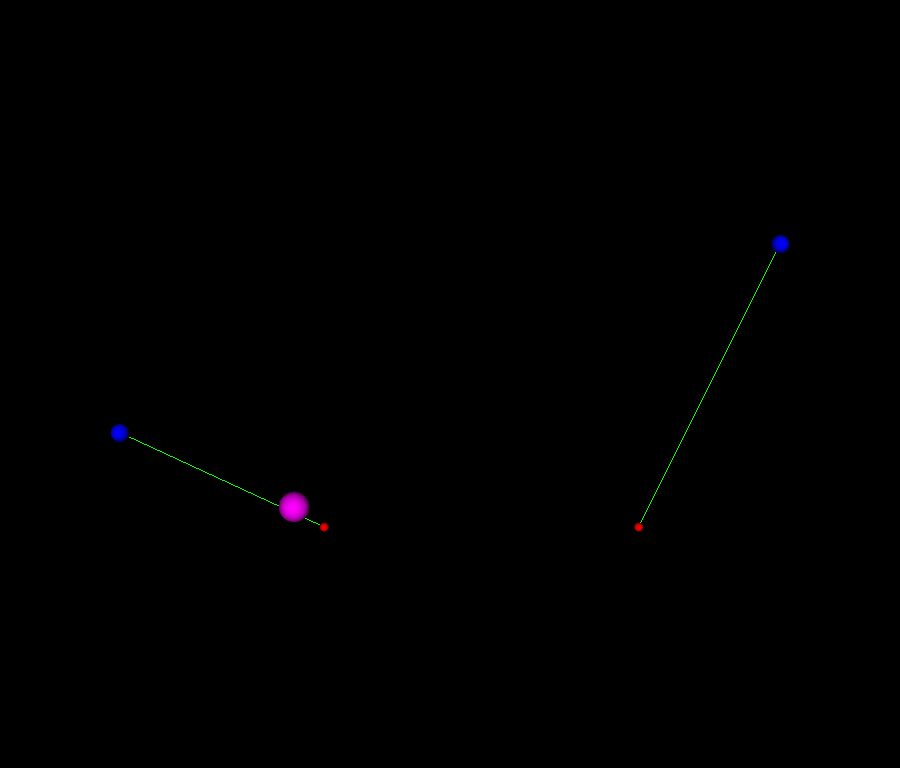
A more complex scene scene#
scene = fury.window.Scene()
show_manager = fury.window.ShowManager(
scene=scene, size=(900, 768), reset_camera=False, order_transparent=True
)
Note: If a control point is set to None, it gets the value of the point it controls.
keyframes = {
# time - position - in control point - out control point
0.0: {"value": [-2, 0, 0], "out_cp": [-15, 6, 0]},
5.0: {"value": [18, 0, 0], "in_cp": [27, 18, 0], "out_cp": [27, -18, 0]},
9.0: {"value": [-5, -10, -10]},
}
Create the sphere actor.
sphere = fury.actor.sphere(np.array([[0, 0, 0]]), (1, 0, 1))
Create an Animation and adding the sphere actor to it.
animation = fury.animation.Animation(actors=sphere)
Setting Cubic Bezier keyframes
animation.set_position_keyframes(keyframes)
changing position interpolation into cubic bezier interpolation
animation.set_position_interpolator(fury.animation.cubic_bezier_interpolator)
visualizing the points and control points (only for demonstration)
for keyframe in keyframes.values():
pos = keyframe.get("value")
in_control_point = keyframe.get("in_cp")
out_control_point = keyframe.get("out_cp")
###########################################################################
# visualizing position keyframe
vis_point = fury.actor.sphere(np.array([pos]), (1, 0, 0), radii=0.3)
scene.add(vis_point)
###########################################################################
# Visualizing the control points and their length (if exist)
for cp in [in_control_point, out_control_point]:
if cp is not None:
vis_cps = fury.actor.sphere(np.array([cp]), (0, 0, 1), radii=0.6)
cline_actor = fury.actor.line(
np.array([[pos, cp]]), colors=np.array([0, 1, 0])
)
scene.add(vis_cps, cline_actor)
Initializing the timeline to be able to control the playback of the animation.
timeline = fury.animation.Timeline(animations=animation, playback_panel=True)
We only need to add the Timeline to the ShowManager
show_manager.add_animation(timeline)
Start the animation
if interactive:
show_manager.start()
fury.window.record(
scene=showm.scene, out_path="viz_keyframe_animation_bezier_2.png", size=(900, 768)
)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.767 seconds)
