Note
Click here to download the full example code
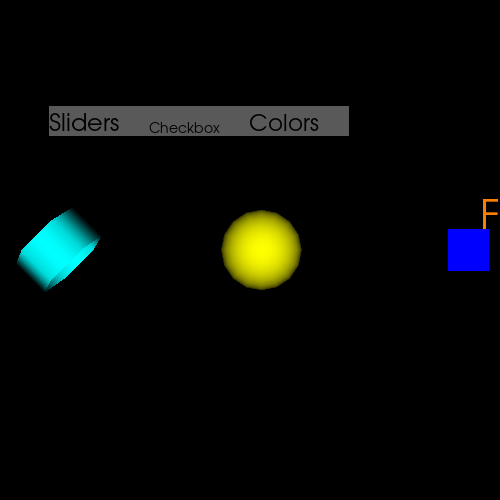
Tab UI¶
This example shows how to use the Tab UI. We will demonstrate how to create Tabs for:
Slider controls for a Cube
Checkboxes for Cylinder and Sphere
Color combobox for Fury.
First, some imports.
from fury import ui, window, actor
import numpy as np
from fury.data import fetch_viz_icons
First we need to fetch some icons that are included in FURY.
Out:
Data size is approximately 12KB
Dataset is already in place. If you want to fetch it again please first remove the folder /Users/koudoro/.fury/icons
First, we create the Tab UI.
Slider Controls for a Cube for Tab Index 0¶
Now we prepare content for the first tab.
ring_slider = ui.RingSlider2D(initial_value=0,
text_template="{angle:5.1f}°")
line_slider_x = ui.LineSlider2D(initial_value=0,
min_value=-10, max_value=10,
orientation="horizontal",
text_alignment="Top")
line_slider_y = ui.LineSlider2D(initial_value=0,
min_value=-10, max_value=10,
orientation="vertical",
text_alignment="Right")
cube = actor.box(centers=np.array([[10, 0, 0]]),
directions=np.array([[0, 1, 0]]),
colors=np.array([[0, 0, 1]]),
scales=np.array([[1, 1, 1]]))
cube_x = 0
cube_y = 0
def rotate_cube(slider):
angle = slider.value
previous_angle = slider.previous_value
rotation_angle = angle - previous_angle
cube.RotateX(rotation_angle)
def translate_cube_x(slider):
global cube_x, cube_y
cube_x = slider.value
cube.SetPosition(cube_x, cube_y, 0)
def translate_cube_y(slider):
global cube_x, cube_y
cube_y = slider.value
cube.SetPosition(cube_x, cube_y, 0)
ring_slider.on_change = rotate_cube
line_slider_x.on_change = translate_cube_x
line_slider_y.on_change = translate_cube_y
After defining content, we define properties for the tab.
tab_ui.tabs[0].title = "Sliders"
tab_ui.add_element(0, ring_slider, (0.3, 0.3))
tab_ui.add_element(0, line_slider_x, (0.0, 0.0))
tab_ui.add_element(0, line_slider_y, (0.0, 0.1))
CheckBoxes For Cylinder and Sphere for Tab Index 1¶
Now we prepare content for second tab.
cylinder = actor.cylinder(centers=np.array([[0, 0, 0]]),
directions=np.array([[1, 1, 0]]),
colors=np.array([[0, 1, 1]]),
radius=1.0)
sphere = actor.sphere(centers=np.array([[5, 0, 0]]),
colors=(1, 1, 0))
figure_dict = {'cylinder': cylinder, 'sphere': sphere}
checkbox = ui.Checkbox(labels=["cylinder", "sphere"])
# Get difference between two lists.
def sym_diff(l1, l2):
return list(set(l1).symmetric_difference(set(l2)))
# Set Visiblity of the figures
def set_figure_visiblity(checkboxes):
checked = checkboxes.checked_labels
unchecked = sym_diff(list(figure_dict), checked)
for visible in checked:
figure_dict[visible].SetVisibility(True)
for invisible in unchecked:
figure_dict[invisible].SetVisibility(False)
checkbox.on_change = set_figure_visiblity
After defining content, we define properties for the tab.
Color Combobox for Fury for Tab Index 2¶
Now we prepare content for third tab.
label = ui.TextBlock2D(
position=(600, 300), font_size=40, color=(1, 0.5, 0),
justification="center", vertical_justification="top",
text="FURY rocks!!!"
)
colors = {
"Violet": (0.6, 0, 0.8),
"Indigo": (0.3, 0, 0.5),
"Blue": (0, 0, 1),
"Green": (0, 1, 0),
"Yellow": (1, 1, 0),
"Orange": (1, 0.5, 0),
"Red": (1, 0, 0)
}
color_combobox = ui.ComboBox2D(items=list(colors.keys()),
placeholder="Choose Text Color",
size=(250, 150), draggable=True)
def change_color(combobox):
label.color = colors[combobox.selected_text]
color_combobox.on_change = change_color
After defining content, we define properties for the tab.
tab_ui.tabs[2].title = "Colors"
tab_ui.add_element(2, color_combobox, (0.1, 0.3))
Define on_change & on_collapsed methods for tab ui to perform certain tasks while active tab is changed or when the tab is collapsed. Note: Tab UI can be collapsed by right clicking on it.
def hide_actors(tab_ui):
if tab_ui.tabs[tab_ui.active_tab_idx].title == "Sliders":
cube.SetVisibility(True)
cylinder.SetVisibility(False)
sphere.SetVisibility(False)
label.set_visibility(False)
elif tab_ui.tabs[tab_ui.active_tab_idx].title == "Checkbox":
cube.SetVisibility(False)
set_figure_visiblity(checkbox)
label.set_visibility(False)
else:
cube.SetVisibility(False)
cylinder.SetVisibility(False)
sphere.SetVisibility(False)
label.set_visibility(True)
def collapse(tab_ui):
if tab_ui.collapsed:
cube.SetVisibility(False)
cylinder.SetVisibility(False)
sphere.SetVisibility(False)
label.set_visibility(False)
tab_ui.on_change = hide_actors
tab_ui.on_collapse = collapse
Next we prepare the scene and render it with the help of show manager.
sm = window.ShowManager(size=(800, 500), title="Viz Tab")
sm.scene.add(tab_ui, cube, cylinder, sphere, label)
# To interact with the ui set interactive = True
interactive = False
if interactive:
sm.start()
window.record(sm.scene, size=(500, 500), out_path="viz_tab.png")
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.166 seconds)