Note
Click here to download the full example code
Visualize surfaces¶
Here is a simple tutorial that shows how to visualize surfaces using DIPY. It
also shows how to load/save, get/set and update vtkPolyData and show
surfaces.
vtkPolyData is a structure used by VTK to represent surfaces and other data
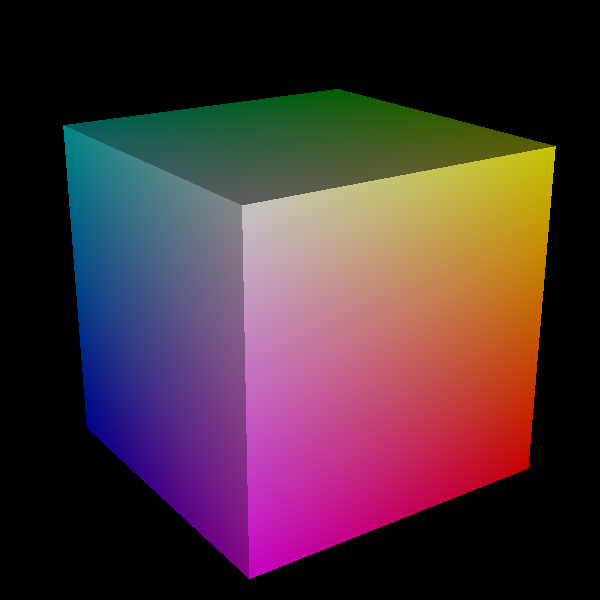
structures. Here we show how to visualize a simple cube but the same idea
should apply for any surface.
import numpy as np
Import useful functions from dipy.viz.utils
import dipy.io.vtk as io_vtk
import fury.utils as ut_vtk
from fury import window
# Conditional import machinery for vtk
# Allow import, but disable doctests if we don't have vtk
from dipy.utils.optpkg import optional_package
vtk, have_vtk, setup_module = optional_package('vtk')
Create an empty vtkPolyData
my_polydata = vtk.vtkPolyData()
Create a cube with vertices and triangles as numpy arrays
my_vertices = np.array([[0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 1.0],
[1.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[1.0, 0.0, 1.0],
[1.0, 1.0, 0.0],
[1.0, 1.0, 1.0]])
# the data type for vtk is needed to mention here, numpy.int64
my_triangles = np.array([[0, 6, 4],
[0, 2, 6],
[0, 3, 2],
[0, 1, 3],
[2, 7, 6],
[2, 3, 7],
[4, 6, 7],
[4, 7, 5],
[0, 4, 5],
[0, 5, 1],
[1, 5, 7],
[1, 7, 3]], dtype='i8')
Set vertices and triangles in the vtkPolyData
ut_vtk.set_polydata_vertices(my_polydata, my_vertices)
ut_vtk.set_polydata_triangles(my_polydata, my_triangles)
Save the vtkPolyData
file_name = "my_cube.vtk"
io_vtk.save_polydata(my_polydata, file_name)
print("Surface saved in " + file_name)
Out:
Surface saved in my_cube.vtk
Load the vtkPolyData
cube_polydata = io_vtk.load_polydata(file_name)
add color based on vertices position
cube_vertices = ut_vtk.get_polydata_vertices(cube_polydata)
colors = cube_vertices * 255
ut_vtk.set_polydata_colors(cube_polydata, colors)
print("new surface colors")
print(ut_vtk.get_polydata_colors(cube_polydata))
Out:
new surface colors
[[ 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 255]
[ 0 255 0]
[ 0 255 255]
[255 0 0]
[255 0 255]
[255 255 0]
[255 255 255]]
Visualize surfaces
# get vtkActor
cube_actor = ut_vtk.get_actor_from_polydata(cube_polydata)
# renderer and scene
renderer = window.Renderer()
renderer.add(cube_actor)
renderer.set_camera(position=(10, 5, 7), focal_point=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
renderer.zoom(3)
# display
# window.show(renderer, size=(600, 600), reset_camera=False)
window.record(renderer, out_path='cube.png', size=(600, 600))
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.114 seconds)